Log Transforms
Transforms allow you to convert your raw log data into RunReveal’s normalized schema. By creating a pipeline of processors, you can extract, modify, and map your log fields to a standardized format.
Transform Pipeline
A transform pipeline consists of a sequence of processors that manipulate your log data. Each processor performs a specific operation, and the output of one processor becomes the input for the next. The final result is mapped to RunReveal’s normalized schema fields.
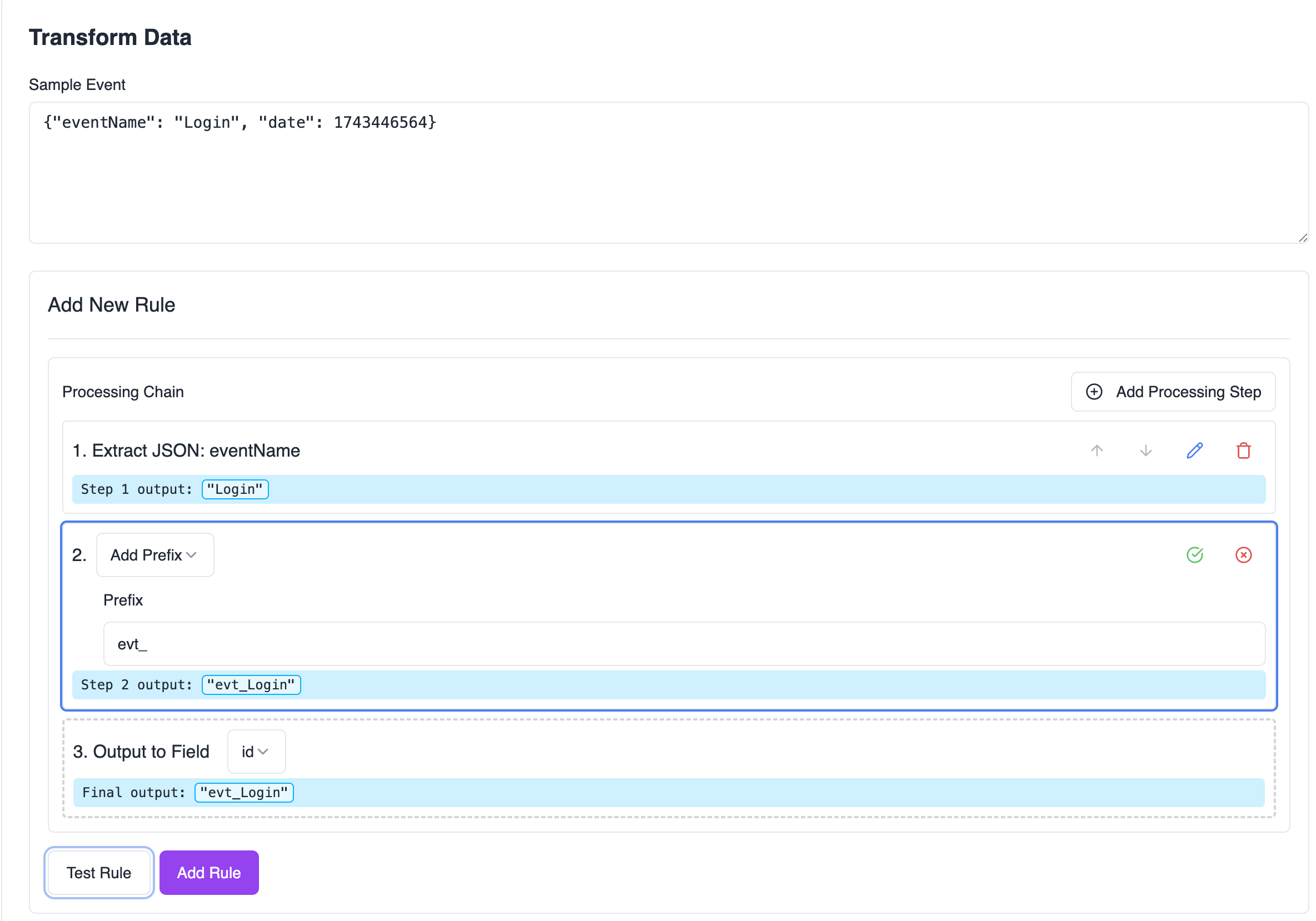
Building Your Pipeline
- Start with your raw log data
- Add processors to extract and transform the data
- Use the Output processor to map the result to a normalized field
- Test your transform with sample data
Available Processors
Text Extraction Processors
Extract JSON Field
- Extracts values from JSON data using GJSON path syntax
- Example: Extract nested fields like
data.user.id
Extract Delimited Field
- Pulls data from delimited text (CSV, TSV, etc.)
- Configurable delimiter and quote handling
- Specify field index to extract
Extract with Regex
- Uses regular expressions to capture specific parts of text
- Supports named capture groups
- Useful for semi-structured log formats
Text Manipulation Processors
Add Prefix/Suffix
- Append text before or after your data
- Useful for standardizing field formats
Convert Case
- Transform text to uppercase or lowercase
- Ensures consistent casing in your schema
Regex Find/Replace
- Find and replace text patterns
- Clean up or standardize text formats
Strip Characters
- Remove specific characters from text
- Clean up unwanted characters or whitespace
Trim Whitespace
- Remove leading/trailing spaces
- Standardize field values
Extract Substring
- Pull specific portions of text by position
- Support for both positive and negative indices
Split String
- Divide text by a delimiter and select a specific part
- Useful for breaking down combined fields
Date/Time Processor
Format Date/Time
- Convert between different date/time formats
- Supports common formats:
- RFC3339
- Unix timestamps (seconds/milliseconds)
- RFC822
- ANSIC
- Custom formats
Output Processor
Output to Field
- Maps transformed data to normalized schema fields
- Available normalized fields include:
- Event fields (id, eventName, eventTime)
- Actor fields (id, email, username)
- Network fields (src.ip, src.port, dst.ip, dst.port)
- Service fields (name)
- Resource and tag fields
Building an Effective Pipeline
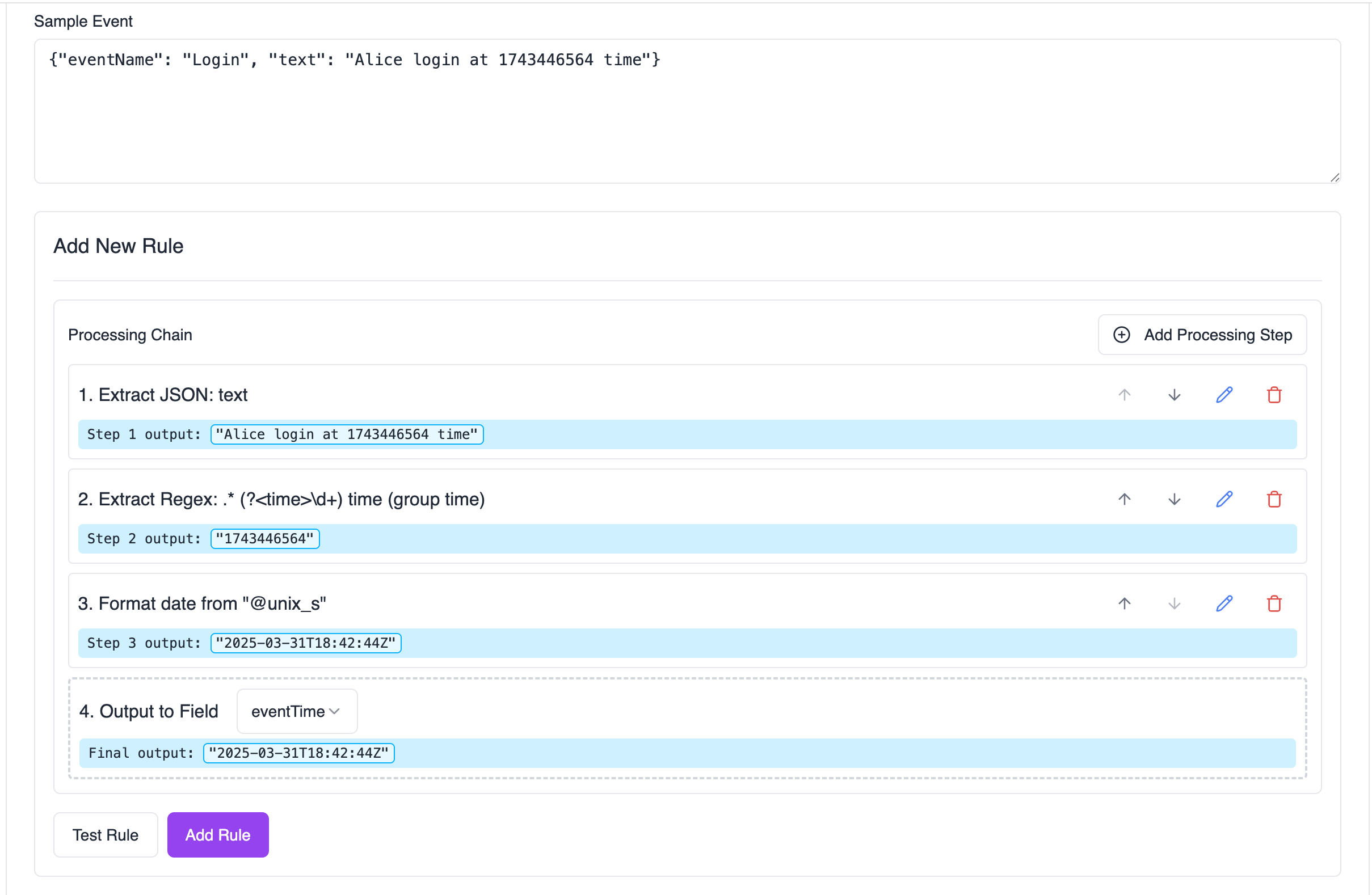
-
Start with Data Extraction
- Use JSON, Regex, or Delimited processors to pull out raw values
- Example: Extract timestamp from a log line using regex
-
Clean and Format
- Apply text manipulation processors to standardize the data
- Example: Convert extracted hostname to lowercase
-
Transform Dates
- Convert timestamps to the required format
- Example: Convert Unix timestamp to RFC3339
-
Map to Schema
- Use Output processor to map to normalized fields
- Example: Map processed IP address to
src.ip
Testing Your Transform
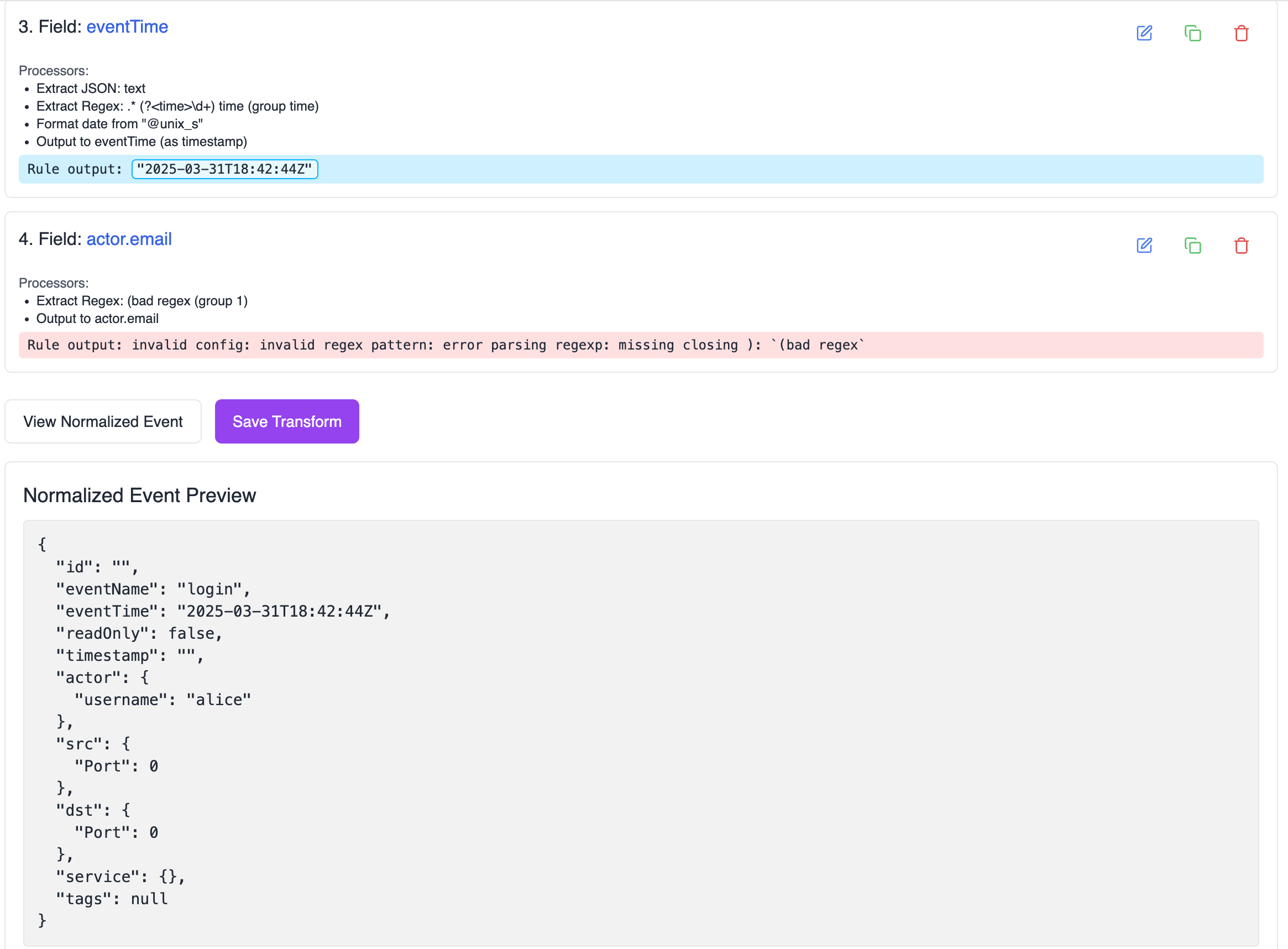
Testing Processors
- Click “Test Rule” to run the sample data through the current rule
- See how each processor affects the data
- View the final normalized output
- Any errors will be highlighted in red
Normalized Schema Preview
- Click “View Normalized Event” to see the entire normalized event that is created when this transform runs
- Ensure your transforms map to the correct fields
- Verify the data types match the schema requirements
Best Practices
-
Build Incrementally
- Add and test one processor at a time
- Verify each step with sample data
-
Test Edge Cases
- Try different log formats
- Include error cases in testing
-
Review Final Output
- Verify all required fields are mapped
- Check data types match schema
Troubleshooting
Common transform issues and solutions:
-
Extraction Failed
- Verify regex patterns against sample data
- Check JSON paths exist in the data
- Confirm delimiter settings match the input
-
Incorrect Output
- Review processor order
- Check field names are exact matches
- Verify date formats
-
Missing Fields
- Ensure all required fields are mapped
- Check for typos in field names
- Verify the transform handles all log variations