Webhooks
RunReveal sends an HTTP POST request to a URL of your choosing whenever a detection fires, a test is triggered, or another notification event occurs.
Set this up from the Notifications page in the RunReveal dashboard.
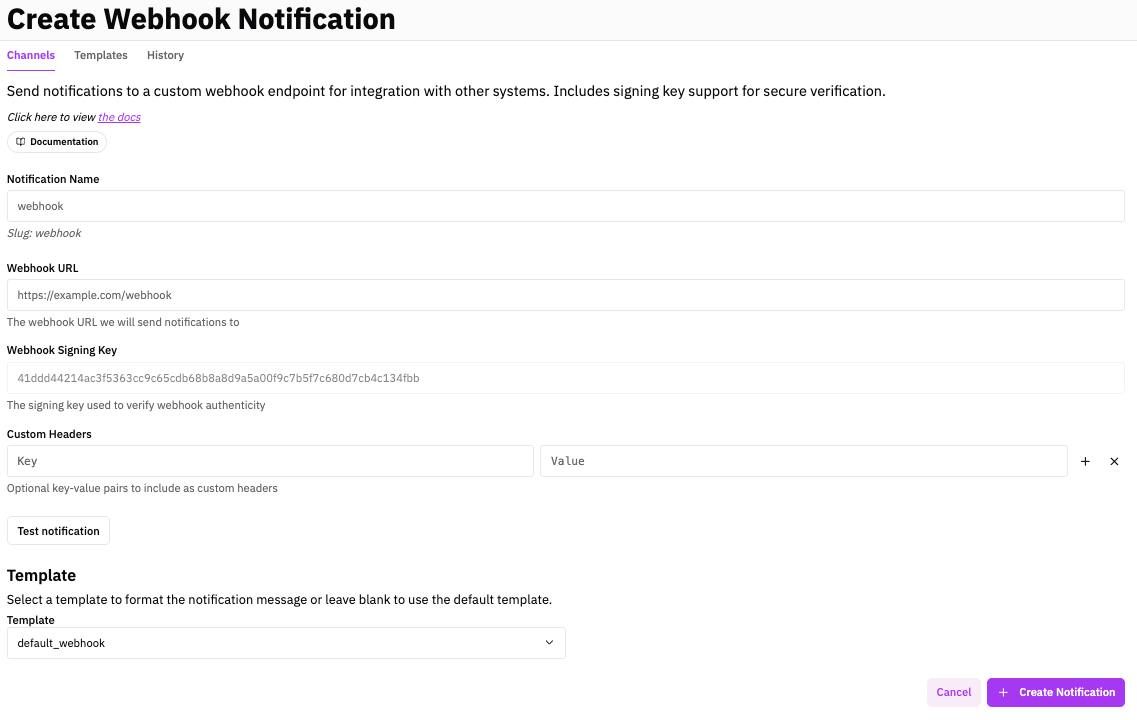
Payload Schema
Every webhook POST body is a JSON object with these top-level fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title | string | Rendered notification title (from template). |
body | string | Rendered notification body (from template). |
channel | string | Notification channel type — always "webhook" for this channel. |
detection | object | Present for detection alerts. See Detection object. |
test | object | Present for test notifications (e.g. {"status": true}). |
data | object | Present for other event types (health checks, user activity, etc.). |
Example payloads
{
"title": "RunReveal Detection Alert: Impossible Travel Detected",
"body": "User [email protected] logged in from two countries within 5 minutes.\n\nSeverity: high\nRows Returned: 1\nResult Link: https://app.runreveal.com/dash/history?alertID=abc123",
"channel": "webhook",
"detection": {
"id": "abc123",
"detectionID": "det_456",
"workspaceID": "ws_789",
"name": "impossible-travel",
"displayName": "Impossible Travel Detected",
"detectionType": "query",
"severity": "high",
"riskScore": 80,
"categories": ["identity"],
"mitreAttacks": ["T1078"],
"mitreTechniques": ["Valid Accounts"],
"description": "Detects logins from geographically distant locations.",
"system": false,
"executedAt": "2025-02-19T12:00:00Z",
"triggered": true,
"resultLink": "https://app.runreveal.com/dash/history?alertID=abc123",
"query": "SELECT actor, srcIP, srcCity FROM events WHERE ...",
"params": { "from": "2025-02-19T11:00:00Z", "to": "2025-02-19T12:00:00Z" },
"runTime": 230,
"resultCount": 1,
"nextRunTime": "2025-02-19T12:15:00Z",
"prevRunTime": "2025-02-19T11:45:00Z",
"results": [
{
"__alertID__": "abc123",
"__columns__": ["actor", "srcIP", "srcCity"],
"actor": "[email protected]",
"srcIP": "203.0.113.42",
"srcCity": "London"
}
],
"columns": ["actor", "srcIP", "srcCity"],
"values": [
["[email protected]"],
["203.0.113.42"],
["London"]
]
}
}Detection object
All detection types share these common fields:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
id | string | Unique execution / alert ID. |
detectionID | string | The detection rule’s ID. |
workspaceID | string | Workspace that owns the detection. |
name | string | Machine-readable detection name. |
displayName | string | Human-readable detection name. |
detectionType | string | "query", "stream", "agent", or "health". |
severity | string | "low", "medium", "high", or "critical". |
riskScore | number | Numeric risk score (0–100). |
categories | string[] | Detection categories. |
mitreAttacks | string[] | MITRE ATT&CK technique IDs. |
mitreTechniques | string[] | MITRE technique names. |
description | string | Detection description. |
notes | string | Optional analyst notes. |
system | boolean | true for managed detections. |
executedAt | string | ISO 8601 execution timestamp. |
triggered | boolean | Whether the detection triggered an alert. |
resultLink | string | Direct link to the alert in RunReveal. |
error | string | Error message, if execution failed. |
Additional fields depend on the detection type:
| Field | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
query | string | The SQL query text. |
params | object | Query parameters (from, to, window). |
runTime | number | Execution time in milliseconds. |
resultCount | number | Number of result rows. |
nextRunTime | string | Next scheduled execution (ISO 8601). |
prevRunTime | string | Previous execution (ISO 8601). |
results | object[] | Row-oriented result objects (each row includes __alertID__, __columns__, and data fields). |
columns | string[] | Column / field names. |
values | any[][] | Columnar result data. |
Webhook Signing
Signing is optional. If no signing key is configured, the RunReveal-Integrity header will contain RUNREVEAL_MESSAGE_UNSIGNED.
When a webhook signing key is set, RunReveal signs every request (including test notifications) so you can verify authenticity.
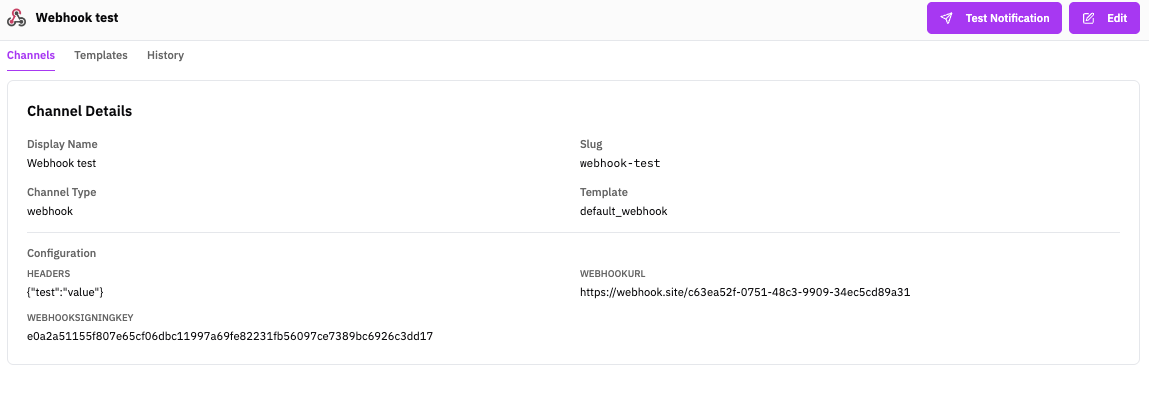
Headers
| Header | Description |
|---|---|
RunReveal-Timestamp | Unix timestamp (seconds) when the webhook was generated. |
RunReveal-Integrity | Base64-encoded HMAC-SHA256 signature, or RUNREVEAL_MESSAGE_UNSIGNED. |
How to verify
Capture the raw request
Read the RunReveal-Timestamp header and the raw HTTP request body bytes. Do not parse the JSON first.
Build the signed payload
Concatenate the timestamp string and the raw body (no separator): <timestamp><body>
Compute the HMAC
Hex-decode your signing key to bytes, then compute HMAC-SHA256 over the concatenated payload. Base64-encode the result.
Compare
Compare your computed signature with the RunReveal-Integrity header using a constant-time comparison.
Verification examples
The following examples include a junk key for demonstration only. Copy and run the test to confirm your verification logic matches RunReveal’s.
import (
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/hex"
"testing"
)
func VerifyWebhook(signingKeyHex, timestamp, integrity string, body []byte) bool {
keyBytes, err := hex.DecodeString(signingKeyHex)
if err != nil {
return false
}
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, keyBytes)
mac.Write([]byte(timestamp))
mac.Write(body)
expected := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(mac.Sum(nil))
a, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(integrity)
b, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(expected)
return hmac.Equal(a, b)
}
// TestVerifySha256 runs a known-good example. The key below is for the example only.
// Run: go test -run TestVerifySha256 -v
func TestVerifySha256(t *testing.T) {
integrity := "iIQEca5cWt6kzKxtjKzBwNYoqRYwcPt2C/2G7VxaglM="
bodyPlusTime := `1720198139{"link":"https://app.runreveal.com/dash/detections/","message":"Yay! Your notification channel was tested successfully.","rawEvent":null,"test":{"status":true},"title":"RunReveal Notification Test"}`
key := "b0c374a4fbfec3ad6047495ca83b4df3d428ed100f51462683c96dcefd74998e"
keyBytes, err := hex.DecodeString(key)
if err != nil {
t.Fatal(err)
}
mac := hmac.New(sha256.New, keyBytes)
mac.Write([]byte(bodyPlusTime))
resultHash := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(mac.Sum(nil))
a, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(integrity)
b, _ := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(resultHash)
if !hmac.Equal(a, b) {
t.Fatalf("integrity check failed: expected match for key+bodyPlusTime")
}
}Signatures are calculated for test notifications too, so you can verify your implementation before going to production.
Related
- Getting Started with Notifications — Set up channels and add to detections
- Notification Channels — All channel types
- Notification Templates — Customize payload content
- Detections — Attach channels to detection rules